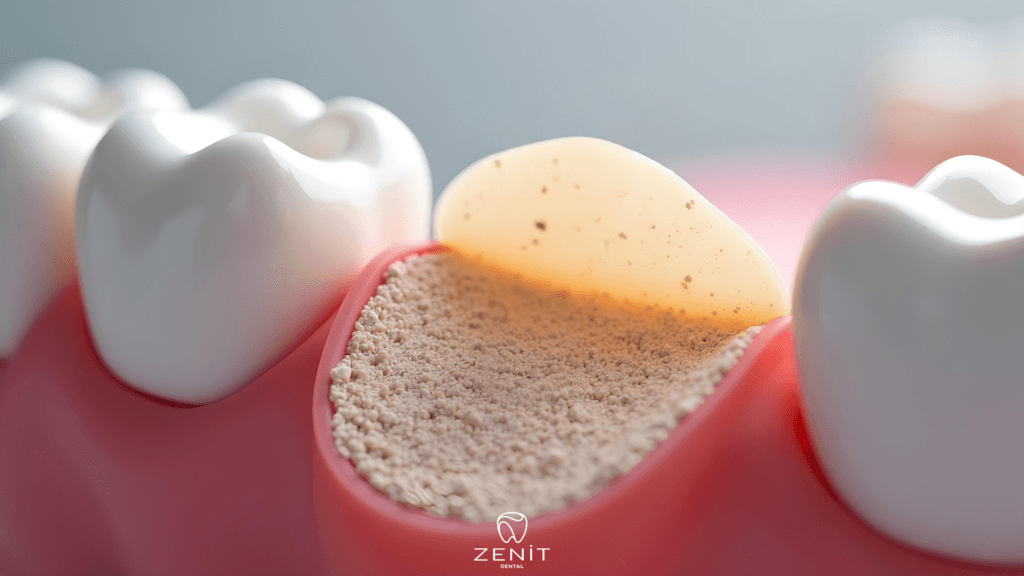
What is Bone Graft?
Bone graft is a frequently used and very important treatment method in the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery. It is mostly applied for the placement of dental implants, treatment of periodontal diseases and reconstruction of bone tissue lost after traumatic injuries. Loss of teeth or loss of jaw bone due to diseases can lead to situations such as not having enough bone tissue to place implants in a healthy way. In such cases, the grafting process comes into play and replaces the missing bone amount, allowing the jawbone to reach the required thickness and height.
The importance of the graft cannot be evaluated only from an aesthetic and functional perspective; This treatment method can also have serious effects on the patient’s general health. Losses in the jawbone may cause deterioration of the facial structure over time and adversely affect chewing and speech functions. In addition, these losses threaten gum health and may lead to increased tooth loss. This procedure prevents such negativities and protects both the patient’s oral health and general quality of life.
How is Bone Graft Applied?
Grafting is performed by placing bone pieces taken from different sources into the missing area. These bone fragments can be obtained from the patient’s own body (autograft), from another person (allograft), from animal origin (xenograft), or from synthetic materials (alloplastic graft).
- Autograft: Bone pieces taken from the patient’s own body, usually from the jawbone, hip or leg bone. This method gives the most reliable results in terms of harmony and integration, because the body does not tend to reject its own tissue.
- Allograft: Bone tissue taken from another person, usually obtained from donors. These bone tissues are transplanted to the patient after going through various sterilization and processing processes. Although allografts do not carry the risk of infection, they may take longer to heal than autografts.
- Xenograft: Bone tissue of animal origin, usually obtained from cattle or pig bones. This type of graft is also sterilized and transplanted to the patient. Xenografts give good results thanks to their natural structure that promotes bone formation.
- Alloplastic Graft: These grafts, produced from synthetic materials, are used to create a structure similar to bone tissue. Alloplastic grafts made from biocompatible materials are easy to accept by the body and the risk of infection is quite low.
In Which Situations Is Bone Graft Applied?
- Dental Implants: After tooth loss, there must be sufficient bone structure to place an implant. If the jawbone is not strong enough to support the implant, bone grafting is necessary. In this way, implants can be placed more firmly and have a longer life.
- Periodontal Diseases: Gum diseases can cause loss of the bone structure that supports the teeth. This causes teeth to become loose and even lost. Bone graft helps support the teeth by compensating for this loss.
- Traumas: Bone losses resulting from accidents or injuries can be repaired with bone grafting. This procedure restores the function and aesthetics of the chin and facial area.
- Congenital Anomalies: Some congenital conditions can cause deficiencies in the jawbone. In these cases, bone grafting can be used to provide functional and aesthetic improvement.
Bone Graft Recovery Time
The healing process after bone grafting may vary depending on the patient’s general health, the source of the graft, and the area where the graft is placed. Usually the recovery period takes between 4 and 6 months. During this process, the bone graft area is expected to heal properly and new bone tissue will form.
It is important for patients to pay extra attention to oral hygiene during this period, avoid smoking and follow the diet and care instructions recommended by their doctors. Antibiotic treatment may be applied to reduce the risk of infection during the healing process.
Bone graft is a very important and widely applied treatment method in the field of dentistry. This procedure, which is used to regenerate missing bone tissue, comes into play when the jaw bone does not have sufficient thickness and density, especially in cases where a dental implant needs to be placed. Loss in the jawbone due to tooth loss, periodontal diseases, trauma or other reasons can lead to bone tissue melting over time and make it difficult to apply treatments such as dental implants in this area. Bone graft strengthens the jawbone in such cases, allowing you to have a healthier mouth structure both aesthetically and functionally.
Bone grafting process helps to preserve and improve the aesthetic structure of the face and jaw, while also ensuring that functions such as chewing and speaking are performed properly. Deficiencies in the jawbone may cause the facial structure to change over time, lips and cheeks to collapse, and overall facial aesthetics to deteriorate. Such situations can have negative effects not only on physical appearance, but also on the individual’s self-confidence and social life. Therefore, bone grafting not only improves your oral health but also improves your overall quality of life.