Gum Disease
Gum diseases, or periodontal diseases, are more common than you might think and affect millions of people worldwide. They are often unnoticed but have significant effects on oral health. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, preventive measures, and some interesting facts about this common dental issue.
What Are Gum Diseases?
Gum diseases encompass a range of conditions that affect the structures supporting the teeth, including the gums and bone. The most common types of gum diseases are gingivitis and periodontitis.
In Detail, Gum Diseases:
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the mildest form of gum disease, often characterized by:
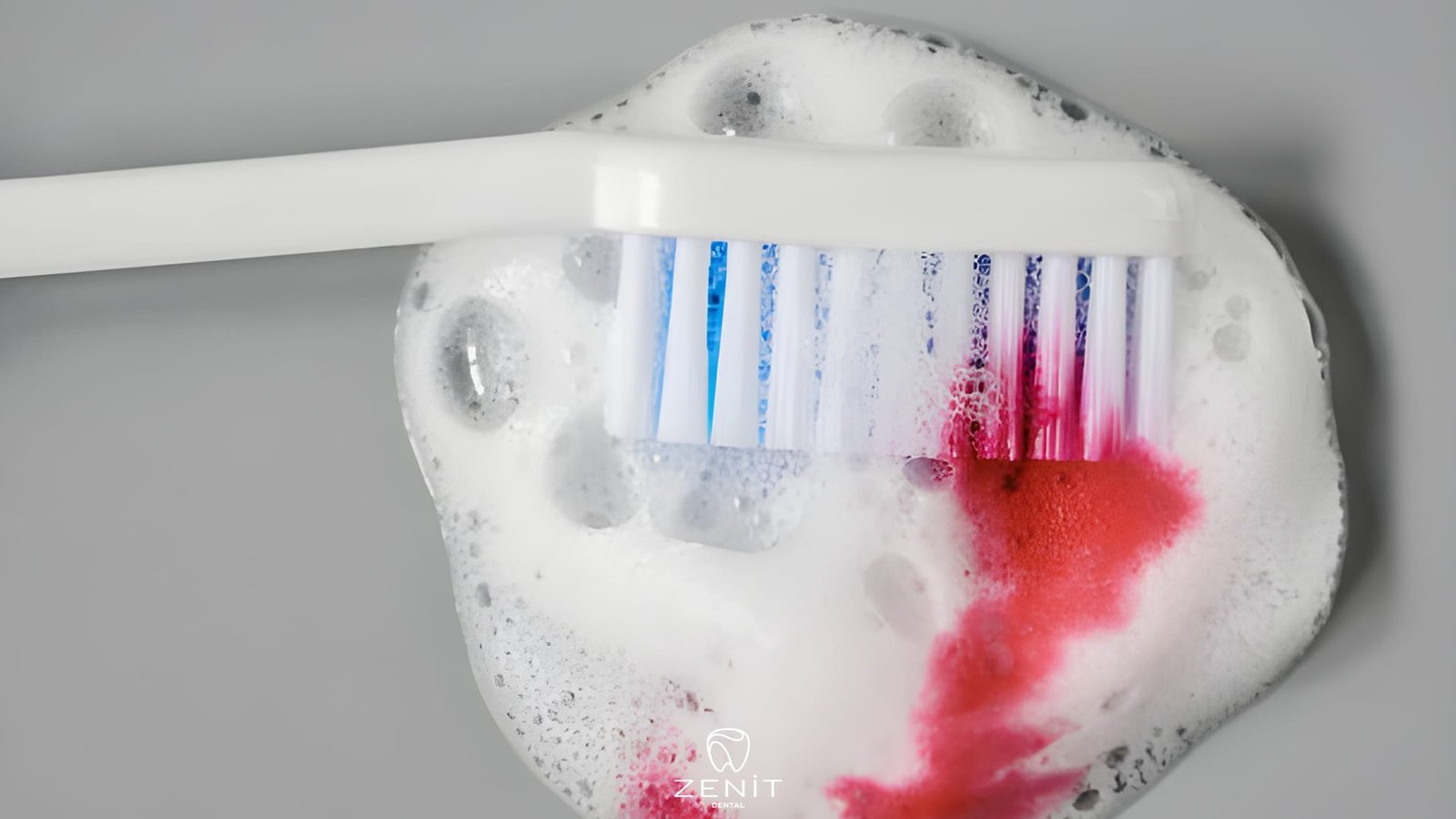
– Bleeding Gums: One of the early signs of gingivitis is bleeding gums noticed during brushing or flossing.
– Swollen Gums: Gingivitis can lead to redness, swelling, and sensitivity of the gums.
– Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath (halitosis) is another common symptom.
Gingivitis is typically caused by poor oral hygiene practices, allowing plaque and bacteria to accumulate on the teeth and gums. It is reversible with good care and regular dental check-ups.
Periodontitis
If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress into a more severe gum disease called periodontitis. Periodontitis is characterized by:
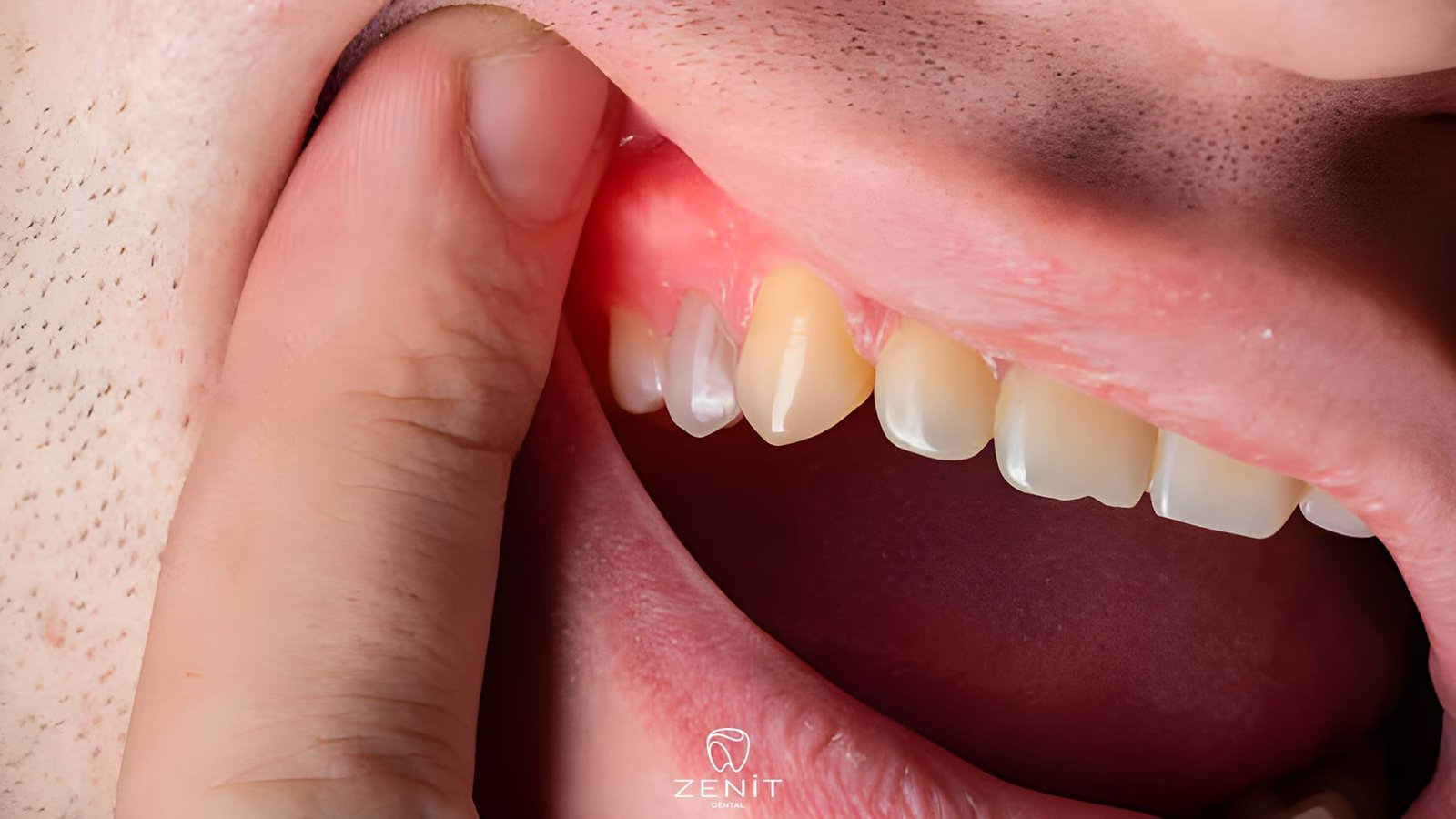
– Receding Gums: Gums may pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected.
– Tooth Mobility: Due to the deterioration of the bone supporting the teeth, they can become loose.
– Bone Loss: Periodontitis can lead to irreversible bone loss, which can result in tooth loss.
Periodontitis requires prompt professional intervention as it can have serious consequences for oral health.

Understanding the causes of gum diseases is crucial for preventive measures. Common risk factors include:
- Inadequate Oral Hygiene: Insufficient brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of plaque.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for gum diseases.
- Genetic Factors: Family history can increase susceptibility to gum problems.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations like pregnancy or menopause can affect gum health.
- Medical Conditions: Some systemic conditions, such as diabetes, can increase the risk of gum diseases.
Preventing Gum Diseases
Preventing gum diseases is all about taking steps to maintain healthy gums. Here are some measures you can take to keep your gums healthy:
- Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day and use dental floss daily to prevent plaque buildup.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visiting your dentist for regular check-ups and professional cleanings is crucial for early diagnosis and prevention.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C, can support gum health.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, consider quitting to reduce your risk of gum diseases.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can affect gum health, so stress management techniques can be beneficial.
- Hormonal Health: If you are experiencing hormonal changes, discuss their impact on oral health with your dentist.
Interesting Facts About Gum Diseases
Now, let’s explore some interesting facts about gum diseases that you may not know and might even surprise you:
- Association with Heart Disease: Research has found a link between gum diseases and heart disease. Inflammation in the gums can contribute to inflammation in the blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart problems.
- Connection to Diabetes: Diabetic patients are more susceptible to gum diseases, and, conversely, gum diseases can make it more challenging to control blood sugar levels. Maintaining good oral health is vital for individuals with diabetes.
- Pregnancy and Dental Health: Pregnant women are more susceptible to dental issues due to hormonal changes. Gum diseases during pregnancy have been associated with preterm birth and low birth weight.
- Alzheimer’s Disease Link: Some studies have suggested a potential link between gum diseases and the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers are investigating this possible connection.
- Hereditary Component: Your genetic makeup can influence your susceptibility to gum diseases. A family history of dental issues can increase your risk.
- Importance of Saliva: Saliva serves as a natural defense mechanism against gum diseases. It contains enzymes that help combat bacteria, protecting your teeth and gums.
- Gingivitis in Children: Gum diseases can develop not only in adults but also in children. This emphasizes the importance of teaching them proper oral hygiene from a young age.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gum diseases are common, often preventable, and can have far-reaching effects on both your oral and overall health. By maintaining good oral hygiene practices, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking professional dental health services, you can keep your gums healthy and your smile bright.
Gum diseases are not just a dental issue; they serve as a window into your overall health. Stay informed, take action, and schedule a check-up right away to ensure a healthy and beautiful smile for everyone.
Comments are closed