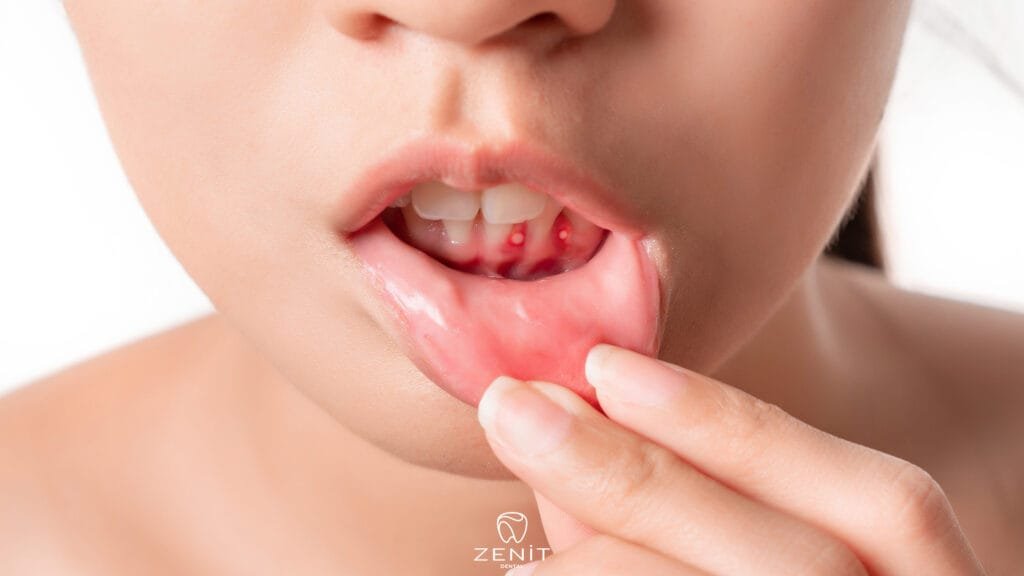
Inflammation in Gums
Gingivitis is a common gum disease that usually occurs as a result of not paying enough attention to oral hygiene. If gingivitis is not detected and treated early, it can lead to more serious gum disease and even tooth loss. This condition is characterized by infection and inflammation of the gum tissue.
The main cause of gingivitis is a sticky, colorless bacterial layer called plaque that accumulates on the surface of the teeth. Plaque is formed by the combination of food debris and saliva. When teeth are not brushed and flossed regularly, plaque accumulates at the gum line, causing irritation of the gums. Plaque that is not cleaned for a long time hardens over time and turns into tartar (tartar), which worsens gingivitis.
What Causes Gingivitis?
Not Paying Attention to Oral Hygiene
The most common cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene. Plaque accumulation occurs on the teeth and gums as a result of not brushing your teeth regularly and not using dental floss. Plaque is a sticky layer filled with bacteria and food debris and causes inflammation in the gums. Plaque adheres to the tooth surface and can turn into tartar over time. Tartar damages the gums, causing inflammation and infection. Inadequate oral hygiene paves the way not only for gingivitis, but also for tooth decay, bad breath and other dental diseases. Therefore, brushing and flossing teeth at least twice a day is critical in maintaining healthy gums.
Smoking
Smoking significantly increases the risk of gum disease. Smoking prevents the gums from accessing oxygen and nutrients, slowing down the healing process and weakening the gum tissues. Additionally, smokers experience more plaque and tartar accumulation in their mouths. Harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke directly damage gum cells and weaken the immune system’s defense mechanism against infections. In addition to gingivitis, serious health problems such as gum recession, dry mouth and oral cancer are more common in smokers. Quitting smoking not only protects gum health, but also positively affects general health.
Hormonal Changes
Women, in particular, experience hormonal changes during periods such as pregnancy, menstrual cycle and menopause. These hormonal fluctuations increase the risk of inflammation of the gums. For example, increased progesterone and estrogen levels during pregnancy can cause gums to become more sensitive to bacteria. Likewise, hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can lead to swelling, redness and bleeding in the gums. During menopause, decreasing estrogen levels can trigger problems such as dry mouth and gum recession. It is important for women to pay more attention to oral hygiene during these periods and not to neglect regular dentist check-ups.
Stress
Stress weakens the immune system, reducing the body’s ability to fight infections. This can lead to various health problems, including gum disease. Individuals under stress may not pay enough attention to oral hygiene and develop unhealthy habits such as smoking and teeth grinding (bruxism). These habits can trigger gingivitis and worsen existing gum disease. Stress management is an important factor in maintaining a healthy lifestyle and gum health. Meditation, exercise and adequate sleep can be effective in reducing stress levels.
Genetic Factors
Some people are genetically more prone to gum disease. People with a family history of gum disease are at greater risk of developing this disease. Genetic factors can affect the immune system’s response to bacteria and infections. This may cause gingivitis to progress faster and turn into more serious gum diseases. Genetic predisposition may require a more aggressive approach to preventing and treating gum disease. These people should pay extra attention to oral hygiene, avoid regular dentist check-ups, and take precautions to protect their gum health.
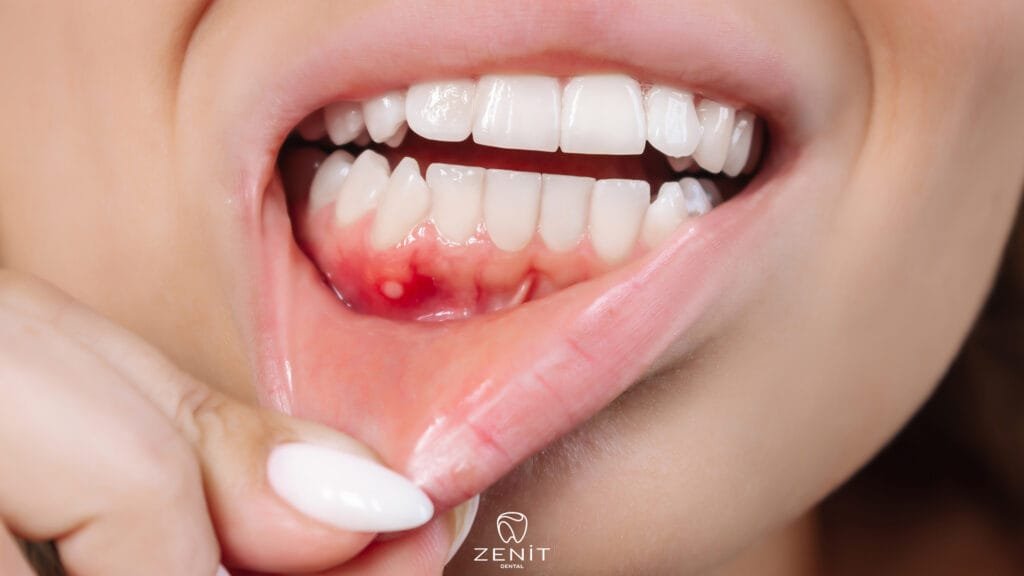
Symptoms of Gingivitis
- Red and Swollen Gums: One of the most obvious symptoms of gingivitis is redness and swollen gums. While healthy gums are pink and firm, inflamed gums have a red and swollen appearance. This redness and swelling is a sign of inflammation of the gums and usually becomes more noticeable during brushing or flossing.
- Bleeding Gums: Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing are common symptoms of gingivitis. Healthy gums do not bleed easily. However, in people with gingivitis, even gentle pressure while brushing or flossing can cause bleeding. This bleeding is a sign that the gums are inflamed and tender.
- Bad Breath: Chronic bad breath is another symptom of gingivitis. Bacteria in the mouth cause bad odor. In people with gingivitis, bacterial plaque and infected gums between the gums can cause bad breath. This condition usually becomes evident in the advanced stages of gum disease.
- Gum Recession: Gums moving away from the teeth and exposing the root surface can be seen in the advanced stages of inflammation. Healthy gums surround and protect the roots of the teeth. However, in people with gingivitis, the gums recede and the root surface of the teeth is exposed. This causes the teeth to appear longer and can lead to tooth sensitivity.
- Loose Teeth: In advanced stages, gingivitis can weaken the supporting tissues of the teeth and cause teeth to loosen. Healthy teeth remain firmly in place with the support of surrounding tissues. However, as gingivitis progresses, the bone and other supporting tissues around the teeth can become damaged, causing loose teeth and even tooth loss. Therefore, when symptoms of gingivitis are noticed, it is important to consult a dentist without delay.
Gingivitis, how is it treated?
Professional Teeth Cleaning
The first step in treating gingivitis is a professional teeth cleaning by your dentist. This process reduces inflammation by removing plaque and tartar accumulation on the teeth. The dentist removes plaque and tartar accumulated on tooth surfaces using special tools and techniques. This process helps remove debris from areas that cannot be reached by brushing and flossing at home. Professional teeth cleaning relieves the symptoms of gingivitis and helps gums regain their health.
Medication
Your dentist may prescribe antibiotics or special mouthwashes to control inflammation. Antibiotics kill bacterial infections, reducing inflammation and speeding up the healing process. Mouthwashes have antibacterial and antiseptic properties and help control microorganisms in the mouth. These medications are used to relieve the symptoms of gingivitis and prevent the spread of infection.
Paying Attention to Good Oral Hygiene
After treatment, it is important to pay attention to oral hygiene to prevent gingivitis from recurring. Brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day. This prevents plaque and tartar build-up and keeps gums healthy. Also, visit your dentist regularly to get professional teeth cleanings and checkups. By monitoring your gum health, your dentist can intervene early and help prevent problems.
Healthy eating
A balanced and nutritious diet supports tooth and gum health. Consuming foods rich in vitamin C, calcium and vitamin D helps strengthen gums. Additionally, consuming fibrous foods helps massage the gums and increase blood circulation. A healthy diet plays an important role in treating and preventing gingivitis.
Reducing Smoking and Alcohol Use
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption play an important role in maintaining gum health. Smoking and alcohol negatively affect the healing process of the gums and contribute to the progression of gum diseases. Smoking reduces blood circulation to the gums and slows down the healing process. Alcohol consumption can cause dry mouth and encourage the formation of bacterial plaque. Therefore, reducing or quitting smoking and alcohol use are important steps to protect gum health.
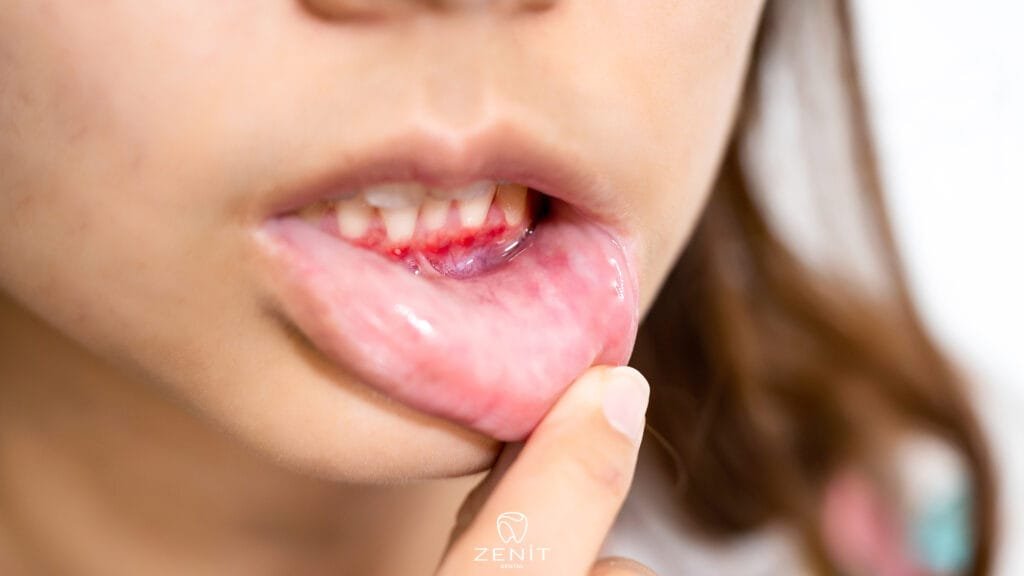

How to Prevent Gingivitis
Regular Teeth Brushing and Flossing
You can prevent gingivitis by brushing and flossing your teeth at least twice a day. These steps prevent plaque and food debris from accumulating between the teeth and at the junction of the gums and teeth. In addition, brushing and flossing with the correct technique keeps the gums healthy.
Dentist Checks
Visiting your dentist regularly is an important way to prevent gingivitis. Professional cleanings and checkups are important to monitor the health of gums and teeth. The dentist can detect signs of gingivitis in the early stages and prevent the problem from progressing by starting treatment.
Healthy eating
A nutritious and balanced diet supports your gum health. You can prevent tooth decay and gingivitis by reducing the consumption of sugary and acidic foods. Additionally, drinking plenty of water maintains oral pH balance and protects your teeth and gums by increasing saliva production.
Non-Smoking
Smoking is one of the most important risk factors for gingivitis. Gum disease is more common and can be more serious in people who smoke. Quitting smoking or staying away from smoking environments are important steps to protect your gum health.
Stress Management
Stress has negative effects on your overall health and can weaken your immune system. This may increase the risk of gum disease. Stress management techniques include activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises and yoga. These techniques reduce stress levels, strengthen your immune system and protect your gum health.
Inflammation in Gums What Causes Gingivitis? Symptoms of Gingivitis Gingivitis, how is it treated? How to Prevent Gingivitis